Due to its nature of work, steel manufacturing requires safe working procedures as workers face many risks on the job. The health and safety of employees should be the top priority for steelmakers since it affects both economic and social factors. Although steel manufacturers have substantially increased their safety procedures over the last decade, many have found it difficult to accelerate progress on this front.
Ever since steel making started, it has been a hazardous process and accidents were unavoidable. Today’s steel companies realize that safety should no longer be unavoidable for an industry which is so modern and technically advanced. Every type of work and process can be made accident-free. This can be achieved with a 100% commitment from everyone, especially from the top management by creating a culture in which safety is the number one priority.
According to a report by the World Steel Association, the top causes of serious incidents across the entire global steel industry are – moving machinery, falling objects, falling from height, asphyxiation or gassing, and cranes.

According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, steel industry workers face the 5th most fatal injuries in their occupation.
Material handling
Material handling comes with a number of risks, especially when it is done manually. Tasks like carrying, lifting, and pushing can make the workplace unsafe for employees. Injuries by material handling can also be quite expensive with lost productivity, medical costs, and decreased employee morale.
Here are some tips on improving productivity in material handling processes:
- Minimizing ergonomic risk factors –The problems that cause unnecessary physical fatigue are the ergonomic risk factors. In material handling, these can be repetitive motions such as frequently reaching and lifting, stressful postures while handling materials, and forceful exertions like lifting heavy loads. Companies can limit the possible risks to employees by identifying such ergonomic risk factors and minimizing them.
- Optimizing space and workflow –Ensuring that every inch of space is utilized to its best advantage will assist in eliminating occurrences of over handling and workflow bottlenecks, whether the material handling systems are used for assembly or storage. This increases efficiency and decreases the possibility of human error.
- Providing personal protective equipment –When workers are provided with protective equipment, it minimizes injuries when moving materials. Protective equipment includes helmets, eye protection gears, gloves, safety boots, metal fiber, etc.
- Getting employee feedback –The best way to improve a process is by getting feedback from the people who actually work in the process. Safety programmes like accident-prevention committees, suggestion schemes, and workers’ safety delegates can be set up to prevent injuries.
- Conducting continuous training –Detailed process instructions in manuals and training videos will help reduce costly errors and ensure that every employee has the appropriate information handy when working on a process.
- Using the right equipment – Using the right equipment in material handling can make the process faster, safer, and efficient.
- Upgrading technology –Replacing old equipment can save utility costs and avoid downtime. Automated technology like sensors and timers can extend the life of the equipment. Using visual aid technology like cameras can further help avoid damage to the equipment and to the person handling it. HoistCam offers such technology which has helped increase efficiency by over 55%.
Material handling in the steel industry
Material handling in the steel industry is about handling hot liquid metals and moving and lifting heavy loads. The equipment used in material handling are exposed to extreme temperatures and conditions, and therefore, safety is of utmost importance when designing solutions.
Here are some of the processes in the steel industry where cranes are used for material handling and how a visual guidance in each of these processes can increase the level of safety:
Smelting – The smelting region of the steel plant is exposed to extreme temperatures. A variety of cranes are used during the smelting of scrap metals. Cranes used in the smelting process are made to lift and carry liquid metals safety. Charge cranes are found in steel-smelting furnace units to load ore or scrap into the furnace. Gantry, overhead, ladle, and turdish cranes are other types of cranes that are installed during the smelting process. Hoistcam overhead crane camera system can be mounted inside the beam of the overhead crane to allow operators to see blind lifts while performing a lift.
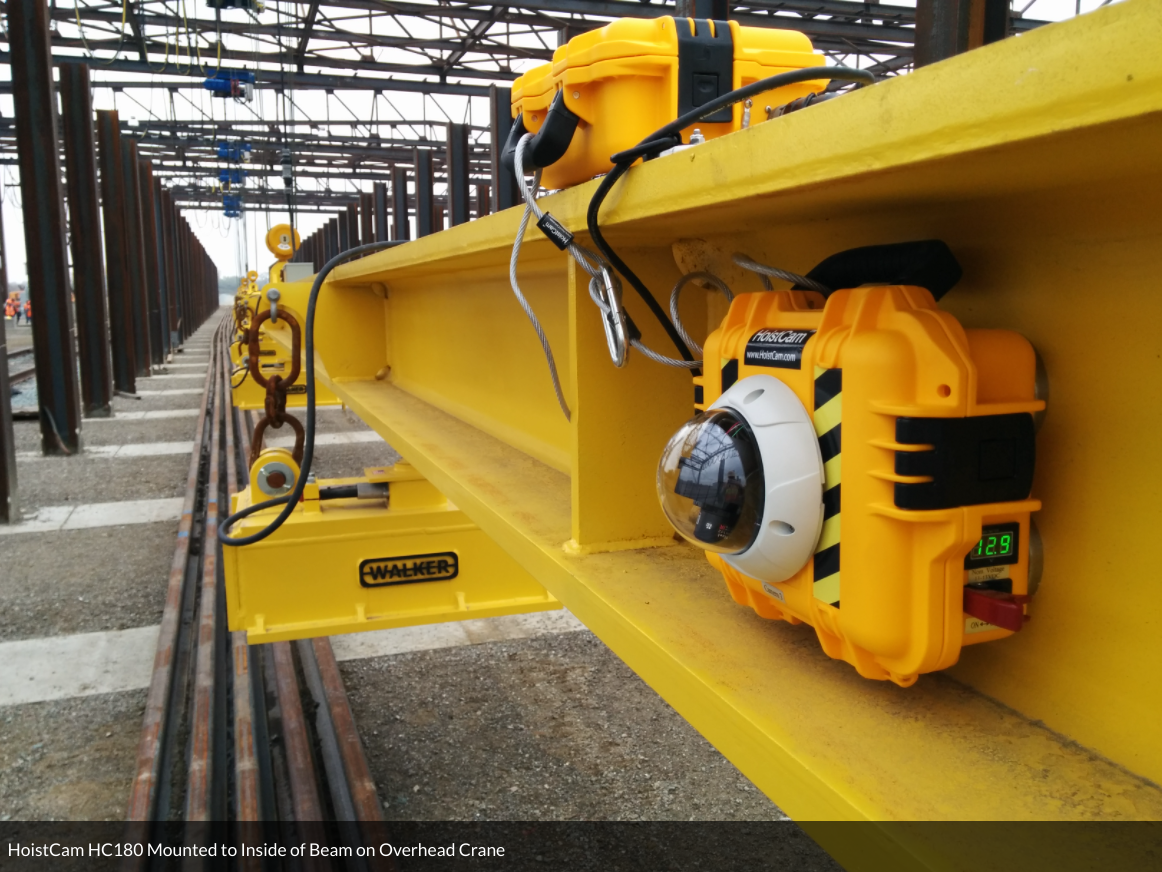

Source: https://hoistcam.com/equipment/overhead-crane/
Scrapyard – This is where the scrap metal arrives for smelting. Gantry cranes or electric overhead cranes are used to unload scrap metal in tonnes, and of different sizes and shapes at the plant. HoistCam provides wireless cameras for rubber tyred gantry cranes that can significantly increase the operator’s view of the load and the surrounding areas during a lift.
Rolling mill–The slabs and billets from the smelters are malleable and hot. They are then moved to the rolling mill for coasting. The cranes used for lifting this hot steel for shaping are equipped with additional capabilities like tongs and detachable magnets. Rotating beam cranes and rotating trolleys are used for such processes. Use of cameras in the rolling mill can help avoid damages to the steel and prevent rework. HoistCam crane cameras provide visual guidance when the hook from the cranes goes down into the center bore of the roll.

Source:
Storage – Overhead cranes are used to move around steel coils in the warehouse and forklifts are used to stack steel products.
There are three priorities for adopting safety practices. They are ethical, financial, and legal. The ethical obligation placed on the management of a steel plant is to ensure a safe workplace. Safe working conditions reduces downtime, promotes systematic working, and improves employee morale, resulting in cost reduction and savings. The legal requirements are defined for safe working. Being proactive and ensuring that safety measures are taken beforehand is key to running a steel company.
References:
- https://hoistcam.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/HoistCam-by-Netarus-Case-Study-Steeled-for-Safety-Picking-Up-Cold-Rolled-without-Damage-to-Person-or-Product.pdf
- http://www.safetytrainingservices.net/sts-blog/bid/280743/safety-in-the-steel-industry-history-hazards-and-how-we-can-help
- https://www.reliableplant.com/Read/31195/material-handling-tips
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330701288_Improving_safety_health_environment_in_steel_industry
- https://www.emech.com/blog/IN/role-of-material-mandling-equipment-in-steel-sector.html
- https://www.westfieldsteel.com/2019/11/material-handling-systems/
- https://www.thermofisher.com/blog/metals/how-to-improve-steel-manufacturing-processes-and-production-methods/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311953484_Innovative_machine_vision_applications_in_steel_industry
- https://www.worldsteel.org/steel-by-topic/safety-and-health.html
- https://www.ispatguru.com/safety-in-a-steel-plant-general-aspects/
- https://www.worldsteel.org/en/dam/jcr:c2726a91-1e5d-4a64-abfe-734a3160b2a7/Safety+and+Health+Position+Paper+2016.pdf

